
The Complete 14 Point Website Audit Checklist
How does one get better at anything?
Practice and hard work, yes. But also rigorous self-reflection.
Looking back at your previous work to determine where and how you can improve is one of the keys to success.
That’s why professional athletes watch game tape of their past performances, and the best authors re-read every draft they write.
The same is true of optimising a website.
If you don’t run a thorough analysis of your website, how will you know what to change to improve your search engine result page (SERP) ranking?
That’s what Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) audits are for.
A website SEO audit is the process of going through the entirety of a website and collecting and analysing data so you can find how to best optimise it.
But where do you even start? How do you know what to look for in a website SEO audit?
There is no one place to start really, but we at Serpwizz put together this 14 point SEO audit checklist to ensure you hit everything.
Gathering Data
The key to an SEO audit is data and statistics.
It tells the story of your website, exactly what is and isn’t doing well and can point you in the direction of what needs to be fixed.
For example, you may notice you have a lot of organic traffic to your homepage, but your click-through rate to your blog is low, which can signal that you need to display your blog more prominently.
So the first thing you should do with a website audit is collect as much data as possible.
Here is how.
Collect Data using Google Analytics and Ahrefs
Start by using Google Analytics, which will give you a ton of numbers on your website and each individual page, such as:
- Organic traffic
- Click-through rate
- Bounce rate
- Average time on page
- Entrances
- Exit rate
- And more
Google Analytics will also show you trends in the above data, as well as give demographics of users such as geographical location and what device was used to access your website.

Source: Google
After Google Analytics, we recommend using ahrefs.
ahrefs will give you data on your keywords and links, including:
- Number of keywords you’re ranking for
- Your ranking for specific keywords
- Number of backlinks and the referring domains
- Number of internal links
- Domain authority

Source: ahrefs
Keyword Analysis
Next up is a keyword analysis.
You should already have some data gathered on your keywords from the previous step. Take that data and compare it with your original set of target keywords and see how well they stack up.
If you notice that you aren’t ranking well for some of your desired keywords, you’ll know where to step up your efforts.
You can also cross-reference this with the data collected by Google Analytics.
Here is an example to show you how you can use these different sets of data together.
Maybe you run a baking website, and you aren’t ranking very well for one of your keywords – let’s say it’s “cookies” – but you are for the keyword “cake.” Then, you notice that your content with “cookies” as the primary keyword doesn’t have a lot of organic traffic, but content with “cake” does.
To fix this, you could add internal links into your “cake” content that send users to your “cookie” content, driving up its organic traffic and helping you rank better for “cookie.”
Once you’ve thoroughly analysed your keywords using data, you can start examining their on-site placement.
Look to see if your keywords are:
- Spread consistently throughout your website and content
- Placed in prominent positions
- Use in headings
- Used as anchor text for links
- Placed in sentences and paragraphs that provide context on your website and business
- Located early and at the top of content
Audit The HTML Of Your Website
HTML is the code that makes up your website.
It’s like the “backside” of a website, and there are certain aspects that need to be optimised for both search engines and users.
Title Tags
A title tag is the heading that is displayed on SERPs for your website and its pages.
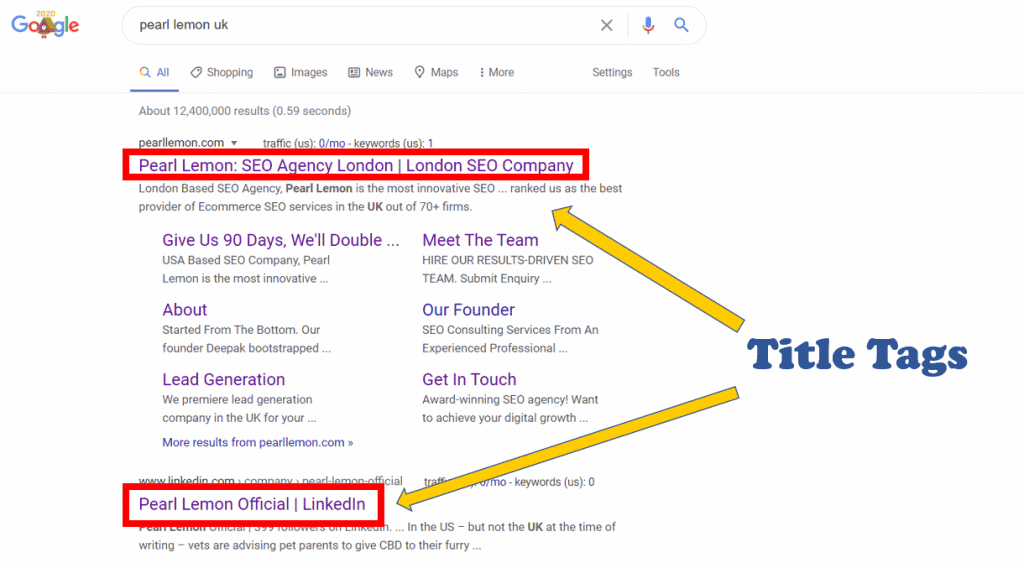
It is used by search engines to index and display your website for relevant searches.
Title tags can also influence potential visitors and entice them to click on your website, so they need to be optimised for both.
When optimising title tags:
- Use keywords (preferably close to the beginning of the title)
- Keep them short and simple
- Clearly define what the page is
- Use punctuation like parenthesis and hyphens to make them easier to read
- Include your business/website name
Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions also appear on SERPs.
They are the descriptions of a page that are located underneath the title tag.
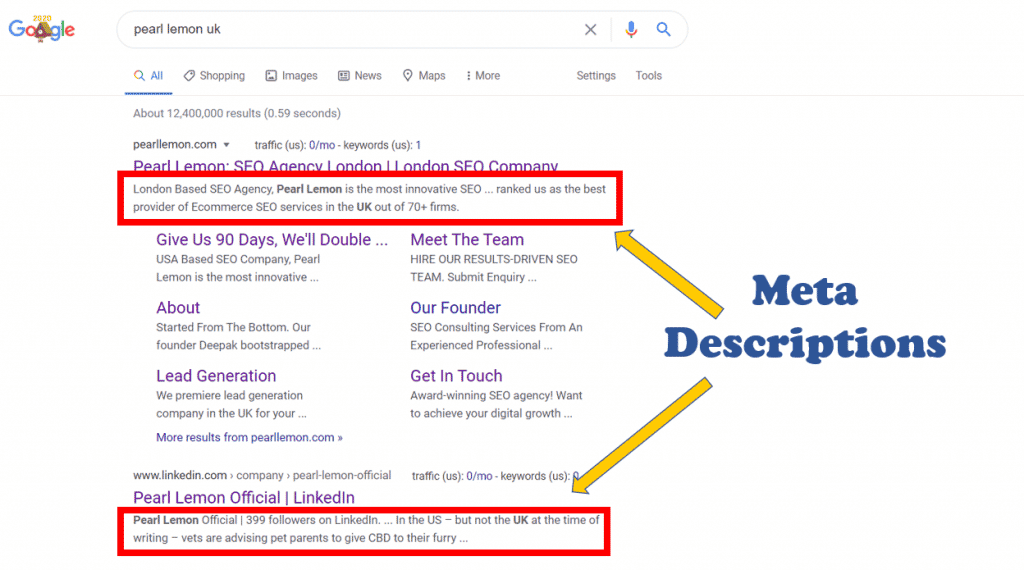
Meta descriptions don’t directly affect search engine rankings like title tags do, but can still influence your click-through rate.
To optimise meta descriptions:
- Include keywords (keywords in meta descriptions get highlighted in bold when they match the search terms)
- Use exciting and/or enticing language
- Explain how the page will give value to the potential visitor
- Be simple and limited to three sentences
- Clearly define what the page is about
Header Tags
Heading tags are the HTML code that represents your section headings on-site and in your content.
See how it says “Header Tags” above? That’s an H2 heading. “Audit The HTML OF Your Website” is an H1 tag.
Using heading tags help organise your website, breaking up your on-page text to make it easier to read and indicating to readers what is to come ahead.
They also can signal to search engines what pages are about and which words are the most important, so be sure to include keywords throughout your headings.
Image Alt Text
Search engines can’t actually see your images, but they can see the image alt text, which is HTML code that describes your image.
The image alt text is also white site readers use when reading your website to blind people.
So make sure your image alt text accurately describes your images using keywords to help search engines and all types of users understand your images.
You can edit the alt text of images using Microsoft Word or Adobe Photoshop.
Check Your Page Speed
Slow loading times are an SEO killer.
People’s attention span these days are so short that if your website doesn’t load in two seconds, you’re looking at a quick bounce my friend (a bounce is when someone leaves your webpage without taking any action).
This leads to a high bounce rate and a low average time spent on-page, both of which will hurt your ranking.
If that wasn’t enough, Google has said that website speed factors into your ranking.
You can check your site speed for free on Google’s PageSpeed Insights.
It will give you data on your website speed for both computers and mobile devices, an overall speed performance score and suggestions on how to improve your site speed.
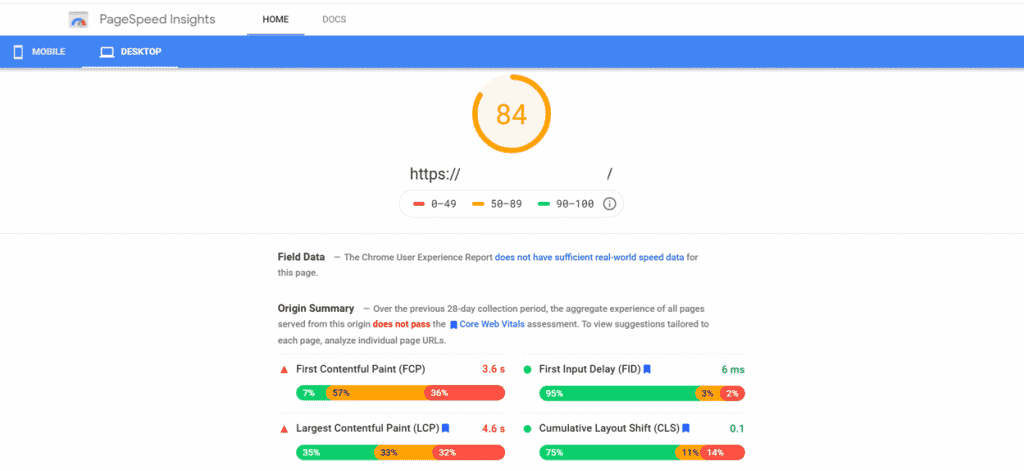
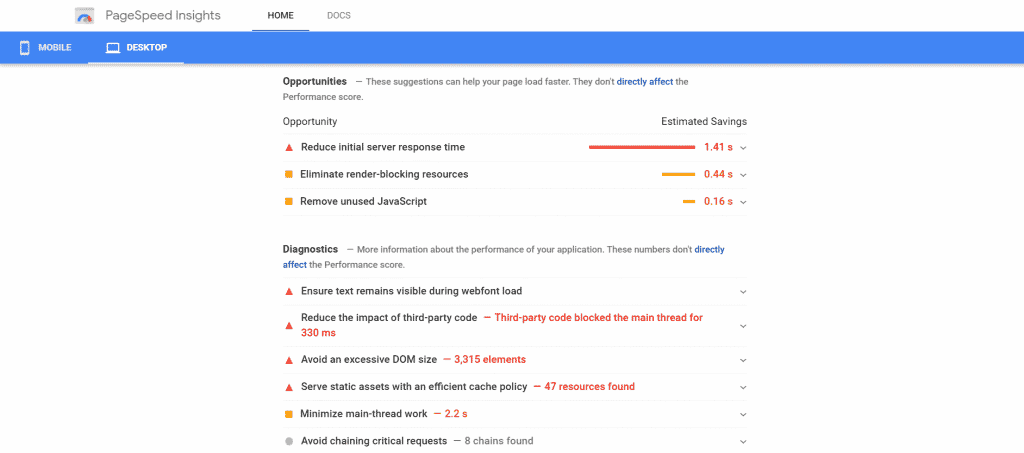
Source: Google
A few other factors you should check that affect website speed are:
- Amount of storage space taken up by a page (ideally it will be around 1 to 2KB)
- Number of images and their file sizes
- Number of plugins
- Redirects
- If Javascript, CSS and HTML are all minified
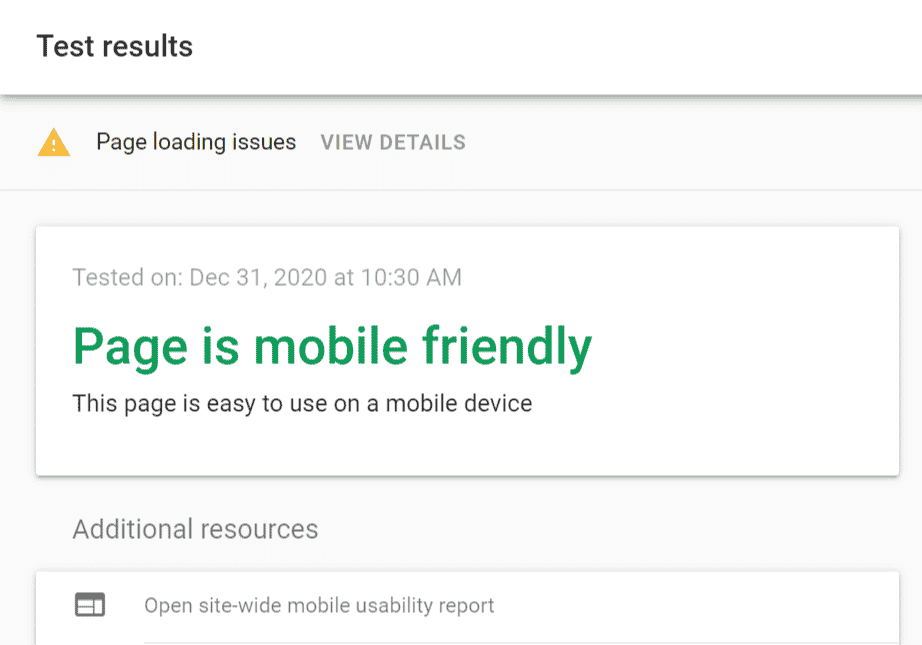
Check The Mobile Friendliness
People don’t just go on computers to look at websites anymore.
According to Statista, 90% of internet users have mobile access now, and if your website doesn’t look good on a cell phone, you’ll be alienating a good chunk of your visitors.
To audit the mobile-friendliness of your website, paste your URL into Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
It will tell you if your site is mobile-friendly or not, as well as a site-wide mobile usability report, breaking your site down even further.
Are Images Optimised?
Images can greatly enhance your website by improving its aesthetic and the presentation of information.
For starters, images are often one of the biggest culprits in slowing down a website due to their larger file sizes when compared to text.
Check the file sizes of your images, and if you need to, compress them using software like Adobe Photoshop or Affinity, and/or limit the number on a page.
Images can also improve the searchability of your website when appropriately optimised.
We already talked about image alt text, but using keywords in the image file name can also help give search engines context to what is contained in a picture. This will be shorter, only 2 to 5 words, but still provides an opportunity to use some more keywords (but don’t keyword stuff).
The text surrounding an image has an impact as well, and it helps to place them near keywords and sentences that are closely related to what you are talking about.
So in addition to alt text, take note of your images file names and placement during your website SEO audit.
For more on optimising images, give our blog titled Overlooked SEO Boosters Part 2: Image & Video Optimisation.
Run An SEO Audit Of Your Blog And Other Content
You should also do a deep dive into your content to see how it is performing.
You can use some of the metrics from Google Analytics talked about previously, but some other things you can check for are:
- Length – Blog posts do the best when they are at least 2,00 words long.
- Keywords – Are you using them throughout your content? In titles and headings? Does each piece of content have a primary keyword?
- Quality – Are your blogs easy to read, informative and engaging?
- Links – You should use both internal and external links in your blog. Ideally, you’ll have an internal link show up first and near the top.
- CTAs – A call to action are specific directions at the end of content with links that encourage further interaction with your site, whether it be more content, to check out your service/product pages or to reach out.
If you can, see if you can get feedback from people on your content using quantitative surveys, as this can be more telling and specific than data.
Check For Indexing Issues
Indexing is essentially the process Google goes through to understand a website by analysing content and cataloguing images and videos.
An indexing issue then is any technical issue that prevents Google from indexing a site or page.
You can check for issues by:
- Going through the HTML code- look specifically for Noindex tags (these may be placed on purpose to hide something, so if you find one for a client, check to see if it’s supposed to be there)
- Seeing if your website has an XML sitemap
- Check if your site has a robots.txt file, which signals which pages Google should and shouldn’t crawl
Look At User Experience

Source: Shutterstock
The user experience for a website is essentially everything that affects the experience while using your website.
A pretty self-explanatory term honestly. I probably didn’t even need to define it, but I wanted to emphasise the fact that it pretty much encompasses EVERYTHING.

Source: Giphy
The goal is for your website to be effortless, easy and straightforward to use.
This encompasses a lot, but here are some things to look for when auditing the user experience of a website:
- Is it easy to navigate and find important information and pages?
- Does it have a fast loading time (already covered)?
- Are the layout and design simple but aesthetically pleasing?
- Are there things to interact with when you land on the site?
- Is there a menu with clearly defined pages?
- Is there on-site customer support available?
Run A Competitor Analysis
Checking out the competition, specifically the successful and high ranking competition, can be one of the best ways to find ways to improve your website.
If you can discover trends among the top ranking websites for your keywords, you can then emulate them on yours to help boost your SEO.
Because if it isn’t working for them, why can’t it work for you?
For example, say you run a website for a fitness gym called Jim’s Gym, and your title tag reads: Jim’s Gym- 24 Hour Gym In London.
But when you google “gyms in London,” you notice that they all have the words “fitness” in their title tags. So you can then change yours to say: Jim’s Gym- 24 Hour Fitness Gym In London.
So take a look at the top ranking websites in your area. You can even run them through tools like ahrefs to get metrics on them that can aid in your analysis.
Find And Fix Broken Links

Source: Pixabay
Broken links – a link that leads to a no-existent page or 404 error- can signal to a visitor that your website is out of date (even if it isn’t).
If you find any broken links on your website, either remove them or replace them with a working link.
You can go through your site link by link to find which ones are broken, or you can use a tool like ahrefs, which will show you all of the links on your website that lead to a 404 error.
Examine URLs
Uniform Resource Locator, or URL, is the website address that appears in the search bar above your website.
URLs are used to help search engines determine what your website is about, so be sure your primary keyword for a page is contained within its URL.
The other thing you is if your URLs are optimised for the user, meaning that they are simple, easy to read, and clearly define what a page is about.
Doing so will not only help a reader get a better understanding of your page but also make them feel safer clicking on it, as complicated URLs are often associated with untrustworthy websites.
Check All Of Your Plugins

Source: Snappygoat.com
Plugins are little add ons that can improve the user experience of your website.
The only problem with them is that they can start to slow your website loading speed down if you have too many.
During your website SEO audit, create a list of all of the plug-ins, add ons and 3rd party tech on your site, and get rid of any that don’t add any value or are unnecessary.
If you’re helping a client out with their website, you can use this tool from SEOptimer to find all of the technology a particular website is built with.
Use An SEO Audit Tool
If you go through this entire checklist, you’ll have completed a full SEO website audit!
You’ll be well on your way to drastically improving the SEO of your website.
If you want to speed this process up, however, in addition to getting more in-depth metrics and analysis could lead to better results, then check out the Serpwizz SEO audit tool.

Our tool will give you a complete SEO audit for your website, as well as several other great tools and add ons that will make optimising your site a breeze.
But don’t take our word for it.
Go see for yourself! You can sign up for our Muggle plan here, which is absolutely free, or try a free trial of one of our premium plans.
And of course, if you have any questions, don’t hesitate to reach out!
Finally, for more great free SEO information, go give other articles on the Serpwizz blog a read!
FAQS
What should be included in a website audit?
Your website audit checklist should include the following:
- Analyzing Design and UX
- Asses Website Content
- On-Page SEO
- Off-Page SEO
- Examin Technical Areas
Here are the top website audit tools.
- SEMrush
- Screaming Frog
- Ahrefs
- OnCrawl
You can either find a company or a tool to do a website audit but you need an SEO website audit checklist before you use a tool.
About The Author

Noah Carey
Noah Carey is a content writer at SERPWizz, and has written such classics as A Beginner’s Guide To Generating Leads The Inbound Way, and How To Turn Whatsapp Into A Power Customer Tool. He also attends the University of Pennsylvania, where he studies English, because he likes reading and writing, and runs for their track and field team because he likes running in circles. For more on Noah, check out his LinkedIn!
